

ÚÜĆšŁÇňż«ňłŤŠëőŠť»ňĺîšÖ犌ęŔ»ŐŠŚęŠ▓╗šÜäňĆĹň▒Ľ´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťňťĘŔ»ŐšľŚńŞşšÜäň║öšöĘńŞŹŠľşňó×ňĄÜŃÇé2020ň╣┤ŠłĹňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║ŔžäŠĘíŔżżňł░254ń║┐ňůâ´╝îšö▒ń║ÄŔ┐ŤňĆúňćůš¬ąÚĽťňÄéňĽćšÜäŠŐÇŠť»ň×䊾ş´╝îňŤŻń║žń╝üńŞÜňŞéňŹášÄçńŻÄń║Ä10%ŃÇéňťĘňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćňč芜»ňÉŽňşśňťĘš▒╗ń╝╝Šľ░Ŕ⯊║ÉŠ▒ŻŔŻŽšÜäň╝»ÚüôŔÂůŔŻŽŠť║ń╝Ü´╝čŠŐÇŠť»Ŕ┐ŤŠşąš╗Öňî╗šöĘňćůš¬ąÚĽťŔíîńŞÜňŞŽŠŁąňô¬ń║ŤňĆĹň▒ĽŔÂőňŐ┐´╝č
ňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚÇÜŔ┐çń║║ńŻôšÜäŔ笚äÂňşöÚüôŠłľš╗ĆŠëőŠť»ń║žšöčšÜäň░ĆňłçňĆúŔ┐Ťňůąń║║ńŻô´╝îńŻ┐šöĘŠŚÂň░ćňćůš¬ąÚĽťň»╝ňůąÚóäŠúÇŠčąšÜäňÖĘň«ś´╝îň╣šŤ┤ŠÄąš¬ąŔžćŠťëňů│ÚâĘńŻŹšÜäňĆśňîľ´╝»ňćůŃÇüňĄľšžĹš▓żš╗ćŠúÇŠčąňĺîňż«ňłŤŠ▓╗šľŚšÜäň┐ůňĄçňĚąňůĚŃÇéŠîëń║žňôüš╗ôŠ×äňĺîňŻóŠÇüňłĺňłć´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťňĆ»ń╗ąňłćńŞ║ŔŻ»ÚĽťňĺîšíČÚĽťŃÇéŠá╣ŠŹ«ńŻ┐šöĘšžĹň«Ąňĺîňť║ŠÖ»´╝îňćŹňłćňłźš╗ćňłćńŞ║Ŕů╣ŔůöÚĽťŃÇüŔâŞŔůöÚĽťŃÇüňů│ŔŐéÚĽť´╝îňĺîŔââÚĽťŃÇüŔéáÚĽťŃÇüŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťšşëŃÇé
Šá╣ŠŹ«ň╝ŚŔőąŠľ»šë╣Š▓ÖňłęŠľçŠĽ░ŠŹ«´╝î2020ň╣┤ńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║ŔžäŠĘíŔżżňł░254ń║┐ń║║Š░ĹňŞü´╝î2015-2020ň╣┤ňĄŹňÉłňó×ÚĽ┐šÄçš║Ž14.2%ŃÇéňÉčňůĘšÉâňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║ŔžäŠĘíń╗Ä164ń║┐šżÄňůâňó×ÚĽ┐Ŕç│215ń║┐šżÄňůâ´╝îň╣┤ňĄŹňÉłňó×ÚĽ┐šÄç5.5%ŃÇéńŞşňŤŻňŞéňť║ňó×ÚÇčŔ┐ťň┐źń║ÄňůĘšÉâ´╝îňťĘňůĘšÉâňŞéňť║šÜäňŹáŠ»öńŞŹŠľşŠĆÉÚźśŃÇéŔâîňÉÄšÜ䊯ťňťĘňÄčňŤáŠś»ňćůš¬ąÚĽťňů╝ňůĚňî╗šľŚŔ«żňĄçńŞÄŔÇŚŠŁÉň▒׊Ǟ´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťńŞ╗Šť║ńŞŹŠśôŠŹčňŁĆ´╝îÚĽťńŻôň»┐ňĹŻń╗Ä6ńެŠťłŔç│10ň╣┤ńŞŹšşë´╝îŠČžšżÄňĆĹŔżżňŤŻň«ÂňĚ▓ň«îŠłÉňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäňłŁŠşąňŞâň▒Ç´╝îňŽéŠŐÇŠť»Š▓튝ëňĄžň╣ůڣꊾ░´╝îňżłÚÜżšťőňł░ňŞéňť║šÜ䊜żŔĹŚňó×ÚĽ┐ŃÇé
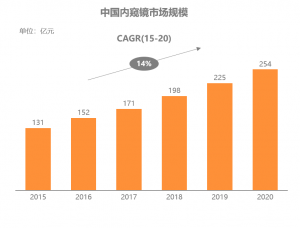
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║ŔžäŠĘí´╝łń║┐ňůâ´╝îń╗ąňç║ňÄéń╗ĚŔ«í´╝ë
ŔÇîńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║Ŕ┐ťŠť¬Úą▒ňĺî´╝îÚÜĆšŁÇŔé┐šśĄŠŚęšşŤňĆŐňż«ňłŤŠ▓╗šľŚňŐáÚÇ芪ŚÚÇĆ´╝îňťĘňĄľń╝üšÜäŠÄĘň╣┐ńŞő´╝îńŻťńŞ║ň┐ůŔŽüšÜäŠúÇŠčąňĺîŠ▓╗šľŚňĚąňůĚ´╝îńŞşňŤŻňî╗ÚÖóń╗ŹňťĘňŐáňĄžň»╣ňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäŔ┤şń╣░ňŐŤň║ŽŃÇéňÉ´╝áŔ«║Šś»šöĘń║ÄŠŚęšÖîšşŤŠčąšÜäŔââÚĽťŃÇüŔéáÚĽťŠúÇŠčą´╝îŔ┐śŠś»ŠĆÉňŹçŠťëňŐęń║ÄňçĆŔŻ╗ŠéúŔÇůšŚŤŔőŽŃÇüŠö╣ňľäÚóäňÉÄšÜäŔůöÚĽťŠëőŠť»ŃÇüš╗ĆŔ笚äÂŔůöÚüôŠëőŠť»´╝îÚâŻÚÜĆšŁÇńŞşňŤŻšÜäŔÇüÚżäňîľňŐáÚÇč´╝îňĺîÚÇÉŠŞÉŠĆÉňŹçšÜäŠÂłŔ┤╣Š░┤ň╣│´╝îŔÄĚňżŚň┐źÚÇčňó×ÚĽ┐ŃÇé
ńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║Šîëń║žňôüš▒╗ň×őŠőćňłć´╝îÚÖĄń║ćšíČÚĽťŃÇüŔŻ»ÚĽťÚĽťńŻô´╝îŔ┐śňîůňÉźšŤŞň»╣ň║öšÜäŔ«żňĄçŃÇüÚŤÂňĄçń╗´╝îń╗ąňĆŐňćůš¬ąÚĽťńŞôšöĘšÜäŔ»ŐšľŚŔÇŚŠŁÉŃÇéňëöÚÖĄŠëőŠť»ŔÇŚŠŁÉšÜäňŻ▒ňôŹ´╝îŠîëšžĹň«Ąš╗ćňłć´╝îŠÖ«ňĄľšžĹňŹáňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║Š»öńżőŠťÇňĄž´╝îň»╣ň║öŔů╣ŔůöÚĽťŃÇüŔâćÚüôÚĽťšşë´╝îŠÂłňîľŃÇüŠ│îň░┐Š»öńżőŠČíń╣ő´╝îňłćňłźň»╣ň║öŔââÚĽťŃÇüŔéáÚĽťŃÇüňŹüń║îŠîçŔéáÚĽťňĆŐŔżôň░┐š«íÚĽťŃÇüš╗ƚܫŔéżÚĽťŃÇüŔćÇŔâ▒ÚĽťšşëÚĽťšžŹŃÇé

ňŤż´╝Ü2020ň╣┤ńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║š╗ćňłć´╝łń║┐ňůâ´╝îń╗ąňç║ňÄéń╗ĚŔ«í´╝ë
ňťĘšź×ń║ëŠá╝ň▒ÇŠľ╣ÚŁó´╝ĹňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║Ŕ󟊌ąš│╗ŃÇüňżĚš│╗ňÄéňĽćň×䊾ş´╝îňŤŻń║žňÄéňĽćňŞéňŹášÄç~5%ŃÇéšö▒ń║Äń╝áš╗čŔŻ»ÚĽťšÜäŠäčňůëňůâňÖĘń╗ÂŔíîńŞÜšö▒ŠŚąń╝üŠÄĘňŐĘňĆĹň▒Ľ´╝îŠáŞň┐âŠŐÇŠť»ňúüň×ĺÚźś´╝îňąąŠ×ŚňĚ┤Šľ»ŃÇüň»îňúźŃÇüň«żňżŚšşëŠŚąń╝üňč║ŠťČň×䊾şŔŻ»ÚĽťňŞéňť║´╝ŤŔÇîňżĚňŤŻňůČňĆŞňŹíň░öňĆ▓ŠëśŠľ»ŠťÇŠŚęŠÄîŠĆíšíČÚĽťšÜäŠč▒šŐÂÚĽťńŻôŠŐÇŠť»´╝îňżĚš│╗ňÄéňĽćńŞÇšŤ┤ń┐ŁŠîüňťĘšíČÚĽťÚóćňččšÜäÚóćňůłňť░ńŻŹŃÇéńŞ╗ŔŽüšÜäňŤŻń║žŔŻ»ÚĽťňĺîšíČÚĽťňÄéňĽć´╝îňŽéň╝Çšźőňî╗šľŚŃÇüŠż│ňŹÄňćůÚĽťŃÇüŔ┐łšĹ×ňî╗šľŚšşëňťĘÚźśšź»ňŞéňť║ńŞŐŠŚáŠ│ĽńŞÄŔ┐ŤňĆúňÄéňĽćšŤ┤ŠÄąšź×ń║ë´╝«ňëŹńŞ╗ŔŽüšŤ«Šáçň«ÜńŻŹń║Äń║îš║žňî╗ÚÖóń╗ąńŞőňî╗ÚÖó´╝îňťĘňĚ▓Ŕ┐ŤÚÖóňî╗ÚÖóńŞş´╝îń╣čŔżâň░ĹńŻťńŞ║ńŞ╗ňŐŤňćůš¬ąÚĽťńŻ┐šöĘ´╝îń╗ŹňťĘň┐źÚÇčŔ┐ŻŔÁÂŔ┐ŤňĆúňÉîŔíîŃÇé
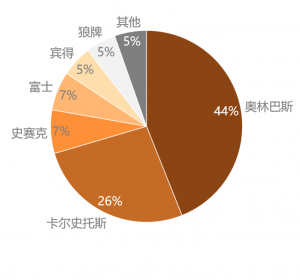
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞşňŤŻňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║šź×ń║ëŠá╝ň▒Ç
ňŤŻń║žňÄéňĽćŔ┐čŔ┐芝¬ňťĘňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćňččšá┤ň▒ÇňĆŹŔÂů´╝îň╝║ŠŐÇŠť»ňúüň×劜»ň»╝Ŕç┤ňŤŻń║žŠŞŚÚÇĆšÄçńŻÄšÜ䚍┤ŠÄąňÄčňŤáŃÇéňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäšáöňĆĹňĺîňłÂÚÇáŠÂëňĆŐňĄÜňşŽšžĹŃÇüňĄÜÚóćňč蚍Şń║ĺÚůŹňÉł´╝îń╗ąŔââŔéáÚĽťŃÇüŔżôň░┐š«íÚĽťńŞ║ń╗úŔíĘšÜäŔŻ»ÚĽťÚŤÂÚâĘń╗ÂňĄÜ´╝îńżŤň║öÚôżňĆŐňůÂňĄŹŠŁé´╝îňłÂÚÇኺąÚ¬Ąš╣üŠŁé´╝áŠ│Ľň«×šÄ░ň«îňůĘšÜäŔç¬ňŐĘňîľŃÇéń╗ąňąąŠ×ŚňĚ┤Šľ»ńŞ║ń╗úŔíĘšÜäšÜ䊌ąš│╗ňćůš¬ąÚĽťňÄéňĽćňžőš╗łň░ćšöčń║žňłÂÚÇáňĚąŔë║ŔžćńŞ║ŠťÇÚźśŠť║ň»ć´╝îň╣ÂňƬňťĘŠŚąŠťČŠťČňťčŔ┐ŤŔíîŠáŞň┐âń║žňôüšÜäšöčń║žŃÇé

ňŤż´╝ÜŔŻ»ŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťš╗ôŠ×䚥║ŠäĆ
ňŤż´╝ÜňůĘšÉâňŤżňâĆń╝áŠäčňÖĘňç║Ŕ┤žÚçĆš╗ôŠ×ä
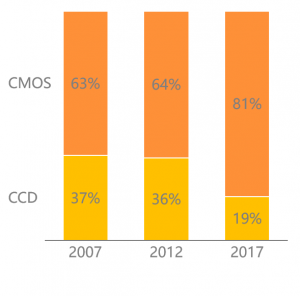
ňťĘCCDŠŚÂń╗ú´╝îCCDŠś»Š×䊳ɚöÁňşÉňćůÚĽťŠłÉŠťČŠťÇÚçŹŔŽüšÜäš╗䊳ÉÚâĘňłć´╝îCCDŠłÉŠťČš║ŽňŹáŠĽ┤ńެňćůÚĽťŠłÉŠťČšÜä40%ŃÇéšö▒ń║ÄCCDŔ«żŔ«íňÄčšÉć´╝îň»╝Ŕç┤ń┐íňĆĚŔżôňç║ŠśôňĆŚňŹĽňâĆš┤ášé╣ňŻ▒ňôŹ´╝îŠĆÉÚźśň║čňôüšÄç´╝îňó×ňŐáňłÂÚÇáÚÜżň║Ž´╝ɊťČÚźśŠśéŃÇéCCDňůĘšŤŤŠŚÂŠťč´╝îń╗ůŠťë6ň«ÂňůČňĆŞňĆ»ń╗ąŠë╣ÚçĆšöčń║ž´╝îňłćňłźńŞ║š┤óň░╝ŃÇüň»îňúźŃÇüŠč»ŔżżŃÇüÚú×ňłęŠÁŽŃÇüŠŁżńŞőňĺîňĄĆŠÖ«´╝îňůÂńŞş4ň«ÂńŞ║ŠŚąń╝ü´╝îÚżÖňĄ┤š┤óň░╝ňŞéňŹášÄçŔÂů50%´╝îŔÇîš┤óň░╝ńŞ║ňąąŠ×ŚňĚ┤Šľ»ŔéíńŞť´╝îń║îŔÇůš╗Ĺň«Üňů│š│╗ň»ćňłç´╝îňůÂń╗ľCCDňÄéň«Âň»╣ŠÁĚňĄľňćůš¬ąÚĽťňÄéňĽćšÜäňç║ňĆúń╣čňĄÜňŐáÚÖÉňłÂŃÇé
šö▒ń║ÄCCDšÜäń╗ĚŠá╝Úźśń╝ü´╝îńŞÇŠŁíň»┐ňĹŻÚĽ┐ŃÇüš╗ôň«×ŔÇÉšöĘšÜäňćůš¬ąÚĽť´╝ÉńŞ║ń║ćňÄéň«Âňĺîňî╗ÚÖóŠľ╣šÜäňů▒ňÉîÚÇëŠőęŃÇéŔÇîŔŻ»ÚĽťň»╣ŠôŹŠÄžŠÇžšÜäŠ×üŔç┤Ŕ┐ŻŠ▒é´╝îńŞÄňĄÜŠČíńŻ┐šöĘňÉÄŠÇžŔâŻŔí░ňçĆšÜäščŤšŤż´╝îŠ×üňĄžŠĆÉÚźśń║ćŔŻ»ÚĽťšÜäňłÂÚÇኳɊťČŃÇéÚÖĄCCDňĄľňůÂńŻÖš▓żň»ćŠáŞň┐âÚâĘń╗šÜäŔŽüŠ▒éń╣čŠ░┤ŠÂĘŔł╣Úźś´╝îŔ┐ÖÚâĘňłćÚŤÂÚůŹń╗ÂńżŤň║öňĽćÚŤćńŞşňťĘŠŚąŠťČňĺîňżĚňŤŻ´╝îňŤŻňćůń╗ŹŠ▓튝ëňŻóŠłÉň«îŠĽ┤šÜäń║žńŞÜÚôż´╝îńŻ┐ňŤŻń║žňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäń║žňôüšź×ń║ëňŐŤńŞŹň╝║ŃÇé

ňŤż´╝Üňî╗šľŚšöĘCMOSňůĘšÉâňç║Ŕ┤žÚçĆ
Šľ░ŠŐÇŠť»CMOSšÜäň╝Ľňůą´╝îňťĘńŞÇň«ÜšĘőň║ŽńŞŐŠĹćŔä▒ń║ćń╝üńŞÜň»╣CCDń╝áŠäčňÖĘšÜäńżŁŔÁľ´╝îňŽéň╝Çšźőňî╗šľŚňťĘ2015 ň╣┤šáöňłÂňç║ňč║ń║ÄCMOSšÜäňŤŻňćůÚŽľňĆ░200ńŞçňâĆš┤ášÜäÚźśŠŞůšöÁňşÉňćůš¬ąÚĽťš│╗š╗č HD-500ŃÇ銍┤ńŞ║ŠČúňľťšÜ䊜»´╝îšö▒ń║ÄCMOSňŞéňť║ŠŤ┤ňłćŠĽú´╝îŠŐÇŠť»ňúüň×嚍Şň»╣ŔżâńŻÄ´╝îÚÇéňÉłňĄžŔžäŠĘíŠë╣ÚçĆšöčń║ž´╝îCMOSšÜäń╗ĚŠá╝ŠŤ┤Šś»ňĹłšÄ░ŠĽ░ÚçĆš║žńŞőŠÄóŔÂőňŐ┐´╝îń╗ÄŔÇîńŻ┐ňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňłÉńŞ║ňĆ»ŔâŻŃÇé
ňŻôňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäŔ«żŔ«íńŻ┐šöĘň»┐ňĹŻń╗ÄŠĽ░šÖżŠČíŔç│ŠĽ░ňŹâŠČíš╝ęščşńŞ║ńŞÇŠČí´╝îńŞöŠŚáÚťÇŔÇâŔÖĹňĆ»š╗┤ń┐«ŠÇž´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜ䊳ɊťČš╗ôŠ×äń╝ÜňĆĹšöčňëžšâłšÜäňĆśňîľŃÇ銼┤ńŞ¬ÚĽťńŻôšÜäŔ«żŔ«íŠÇŁŔĚ»ń╗ÄńŞÇńެš▓żň»ćšÜ䊝║Šó░Ŕ«żňĄç´╝îŔŻČňĆśńŞ║ńŞÇŠŁíŠÖ«ÚÇÜšÜäńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňî╗šöĘň»╝š«í´╝îňÉŠŁÉŠľÖÚÇëšöĘńŞŐń╣芝ëňĄžň╣ůňĆśňîľ´╝îÚçĹň▒׊ŁÉŔ┤ĘŔóźňíĹŠľÖŠŁÉŔ┤ĘŠëÇňĆľń╗ú´╝îÚŤÂÚůŹń╗šÜ䊼░ÚçĆňĄžň╣ůňçĆň░ĹŃÇéń╝áš╗čšÜäňćůš¬ąÚĽťňÄéňĽćň░ÜŠŚáŠÜçň║öň»╣ńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůÚĽťšÜäňć▓ňç╗´╝îŔÇîňÉÄŔÁĚń╣őšžÇŠ│óňúźÚí┐šžĹňşŽňĺîńŞ╣Ú║ŽAmbu´╝îňŞŽšŁÇŠĽ░šÖżńŞçń╗Âň╣┤ń║žÚçĆňî╗šľŚŔÇŚŠŁÉšÜäšöčń║žš╗ĆÚ¬î´╝îšÖ╗ńŞŐń║ćňÄćňĆ▓Ŕł×ňĆ░´╝îňŤŻń║žňÄéňĽćń╣čňąőŔÁĚšŤ┤Ŕ┐Ż´╝îňťĘňŤŻÚÖůńŞŐňŹáŠťëń║ćńŞÇňŞşń╣őňť░ŃÇé
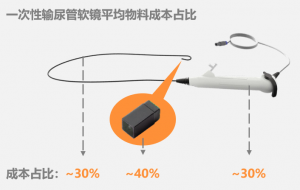
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔŻ»ÚĽťň╣│ňŁçŠłÉŠťČšĄ║ŠäĆ
ňćůš¬ąÚĽťŠś»šŤ┤ŠÄąńŞÄŠéúŔÇůšÜäšÜ«ŔéĄŃÇüÚ╗ĆŔćťňĆŐŠŚáŔĆîš╗äš╗çň»ćňłçŠÄąŔžŽšÜäňî╗šľŚňÖĘŠó░´╝îńŻćšö▒ń║Äňćůš¬ąÚĽťš╗ôŠ×äńŞşňîůňÉźňĄÜńެň░ĆŔÇîÚĽ┐šÜäň╝ÇŠöżÚÇÜÚüô´╝îńŞ║ňż«šöčšëęŃÇüňłćŠ│îšëęňĺîŔíÇŠÂ▓šÜ䊫őňşśńŞÄń║ĄňĆëŠäčŠčôŠĆÉńżŤń║ćšÄ»ňóâ´╝îń║ĄňĆëŠäčŠčôŠłÉńŞ║ÚÜżń╗ąÚü┐ňůŹšÜäňî╗šľŚń║őŠĽůÚúÄÚÖęŃÇ隍Şňů│ňşŽŠť»šáöšęŠśżšĄ║´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťňťĘňî╗šľŚňÖĘŠó░ń║ĄňĆëŠäčŠčôÚúÄÚÖęŠÄĺŔíťńŞşńŻŹňłŚšČČńŞÇ´╝î70%ń╗ąńŞŐšÜäňćůÚĽťňşśňťĘŠŞůŠ┤ŚńŞŹň╣▓ňçÇšÜäÚŚ«Úóś´╝îŠÄąŔ┐ĹňŤŤňłćń╣őńŞëšÜäňŞŞšöĘňćůÚĽťŔóźš╗ćŔĆîŠ▒íŠčôŃÇé
ňťĘňŤŻňćů´╝îń╣čňŞŞŔžüňł░ŔââÚĽťň«ĄŠÂłŠ»ĺŠĽłŠ×ťńŞŹŔżżŠáçŃÇüŔââÚĽťšöčšëꚍŊÁőńŞŹňÉłŠá╝šÜäŠŐąÚüô´╝îňÉŠťëŠŤ┤ňĄÜšÜäÚÖóŠäčňŤáńŞ║ňĆĹšÄ░ńŞŹňĆŐŠŚÂŠ▓튝ëŠŐąňç║ŃÇéňťĘŠťČŔŻ«Šľ░ňćášľźŠâůńŞş´╝îňĄÜň«Âňî╗ÚÖóšÜäňćůÚĽťň«ĄňĺîňĆúŔůöšžĹŃÇüń║öň«śšžĹńŞÇŔÁĚňüťŔ»Ő´╝îń╣čŔ»┤ŠśÄń║ćÚÖóŠľ╣ň»╣ňćůÚĽťň«ĄÚÖóŠäčÚúÄÚÖęšÜäŠőůň┐âŃÇé

ňŤż´╝ÜšżÄňŤŻŠÇąŠĽĹňî╗ňşŽšáöšęŠëÇECRI ňŹüňĄžňî╗šľŚŠŐÇŠť»ňŹ▒ň«│
2021ň╣┤1ŠťłŠťÇŠľ░ňĆĹŔíĘšÜäšáöšęŠśżšĄ║´╝öŔżâňĆ»ÚçŹňĄŹńŻ┐šöĘňĺîńŞÇŠČíŠÇžńŻ┐šöĘšÜäŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽť´╝îńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůÚĽťš╗äšÜäńŻĆÚÖóňĄęŠĽ░ňĺîŠŐŚšöčš┤áŠ▓╗šľŚŠŚÂÚŚ┤ŠŤ┤ščş´╝îŠÇ╗ň╣ÂňĆĹšŚçňĆĹšöčšÄçňĺîŠÇ╗ńŻôŠť»ňÉÄŠäčŠčôšÄçÚ⯊Ť┤ńŻÄ´╝ŤňťĘńŻ┐šöĘńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜä90ńżőŠéúŔÇůńŞş´╝îŠ▓튝ëŠéúŔÇůňç║šÄ░ň░┐Š»ĺšŚçŠłľŔíÇŠÂ▓ňč╣ňů╗ňĹłÚś│ŠÇž´╝îŔÇîň»╣šůžš╗äňç║šÄ░ń║ć3ńżőÚś│ŠÇžŃÇ銝ëňŐŤňť░Ŕ»üŠśÄń║ćńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íÚĽťšÜäńŻ┐šöĘňůĚŠťëŠśÄŠśżÚÖŹńŻÄŠť»ňÉÄň╣ÂňĆĹšŚçňĺîŠäčŠčôšÄçšÜäšë╣šé╣ŃÇé
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚÖŹńŻÄŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŠť»ňÉÄŠäčŠčôšÄç
ňÉ´╝îňťĘňŤŻňćůňî╗ÚÖóšÜäňĚąńŻťÚçĆńŞő´╝îňĄÜŠČíŃÇüňĄÜŠö»ňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäÚçŹňĄŹŠ┤ŚŠÂłń╝ÜÚÇኳÉÚçŹňĄŹńŻ┐šöĘňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäŠÇžŔâŻńŞőÚÖŹšöÜŔç│ŠŹčňŁĆŃÇéŔÇîńŻ┐šöĘńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽť´╝îňĆ»ń╗ąń┐ŁŔ»üŠ»ĆŠČíŠőćň╝ÇňîůŔúůšÜäňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚâŻňťĘňůŠťÇńŻ│šŐŠÇü´╝îńŞÇň«ÜšĘőň║ŽńŞŐŠĆÉÚźśń║ćŠëőŠť»ŠĽłšÄçŃÇé
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚÖŹńŻÄŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŠëőŠť»ŔÇŚŠŚÂ
ňÉ´╝îň»╣ń║Äň╣┐ňĄžšÜäňÄ┐š║žňĆŐń╗ąńŞőňč║ň▒éňî╗ÚÖó´╝îÚŁ×ňŞŞÚÇéňÉłň╝Çň▒Ľš╗ĆŔ笚äÂŔůöÚüôšÜäŠúÇŠčąňĺîŠ▓╗šľŚŠť»ň╝Ć´╝îň»╣Ú║╗ÚćëŃÇüňĄľšžĹšÜäŔŽüŠ▒éń╣čŔżâň╝ÇŠöżŠëőŠť»ŠŤ┤ńŻÄŃÇéňťĘňĆĹŔżżňŤŻň«Â´╝ŞňŻôŠ»öńżőšÜäňćůÚĽťŠúÇŠčąňĺîŠëőŠť»ňťĘÚŚĘŔ»ŐŠłľńŞôšžĹňćůÚĽťńŞşň┐âň«îŠłÉŃÇéŔÇîňťĘňŤŻňćůňč║ň▒éňî╗ÚÖó´╝îňč║ň╗║ŠŐĽňůąńŞŹŔÂ│ÚÖÉňłÂń║ćňćůÚĽťŔ»ŐšľŚšÜäňĆĹň▒ĽŃÇé
ňÉîŠáĚń╗ąŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťňĆľšč│ŠëőŠť»ńŞ║ńżő´╝îňŽéńŞÇň«Âňî╗ÚÖóŔŽüŠľ░ň╝ÇŠşĄŠť»ň╝Ć´╝îÚťÇÚççŔ┤ş2ŠŁíŔ┐ŤňĆúŔŻ»ÚĽťňĆŐńŞÇňĆ░ńŞ╗Šť║´╝îŔ┐ŤÚÖóń╗Ěš║Ž200ńŞçňůâ´╝ŤŔÇîÚÇëŠőęńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽť´╝îň╝Çň▒ĽŠëőŠť»ń╗ůÚťÇÚççŔ┤şŠĽ░ŠŁíňŤŻń║žńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔŻ»ÚĽťňĆŐńŞÇňĆ░ńŞ╗Šť║´╝îŔ┐ŤÚÖóń╗ĚňĆ»ń╗ąŠÄžňłÂňťĘ10ńŞçňůâń╗ąňćůŃÇéńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚŁ×ňŞŞŠťëňłęń║ÄňćůÚĽťŠëőŠť»ňťĘňč║ň▒éňî╗ÚÖóšÜäŠÄĘň╣┐ŃÇé
š╗ĆŔ┐çňĄľŔÁäńŞÄňŤŻňćůń╝üńŞÜňĄÜň╣┤šÜäŠÄóš┤ó´╝îńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňĚ▓ňťĘňĄÜńެň║öšöĘÚóćňččšŤŞŠ»öÚçŹňĄŹńŻ┐šöĘňćůÚĽťŠŤ┤ńŞ║š╗ĆŠÁÄŃÇéňŽéń╝áš╗čŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŠëőŠť»´╝îŔÇâŔÖĹňł░ŔŻ»ÚĽťšÜäň»┐ňĹŻŃÇüš╗┤ń┐«ÚóĹšÄç´╝îňŹĽŠČíŠëőŠť»šÜ䊳ɊťČŔÂůŔ┐ç1.2ńŞçňůâ´╝îŔÇîńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťšÜäňŤŻňćůňůąÚÖóń╗ĚŠá╝ńŞÇŔłČňťĘńŞçňůâń╗ąńŞő´╝îňÉÂň»╣ňî╗ÚÖóŠŁąŔ»┤´╝îńŞÄňćůÚĽťšŤŞňů│šÜ䊳ɊťČŠŤ┤ňŐáňĆ»ŠÄžŃÇé

ňŤż´╝ÜÚçŹňĄŹńŻ┐šöĘŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťňŹĽňĆ░ŠëőŠť»ň╣│ňŁçŠłÉŠťČ´╝łňůâ´╝ë
š▒╗ń╝╝šÜä´╝îň»╣ń║ÄŔćÇŔâ▒ÚĽť´╝îšö▒ń║ÄŔ┐ŤňĆúšÜäŔćÇŔâ▒šöÁňşÉÚĽťŠłÉŠťČŔ┐çń║ÄÚźśŠśé´╝îňťĘňŤŻňćůŠÖ«ňĆŐšÄçňżłńŻÄ´╝îňůëňşŽšíČÚĽťń╗ŹŠś»ńŞ╗ŠÁüŃÇéńŞÇŠČíŠÇžšÜäšöÁňşÉŔćÇŔâ▒ňŹŐšíČÚĽť´╝┤ňżäŠŤ┤š╗ć´╝ëń║▓Š░┤ŠÂéň▒é´╝îŠéúŔÇůńŻôڬ┤ňąŻ´╝îňÉšö▒ń║ÄšöÁňşÉÚĽťŠťëŠŤ┤ÚźśšÜäŠöÂŔ┤╣Šáçňçć´╝îšžĹň«ĄňŹĽŠČíŠëőŠť»ŠôŹńŻťšÜäňłęŠÂŽń╣芝ëń║ćŠö╣ňľäŃÇé
ňŤż´╝Üń╝áš╗čňůëňşŽŔćÇŔâ▒ÚĽťńŞÄńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔćÇŔâ▒ÚĽťŠöÂŔ┤╣ńŞÄňłęŠÂŽň»╣Š»öńŞżńżő´╝łňůâ´╝ë
ń╗ÄńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťšÜäńŻ┐šöĘň»┐ňĹŻŃÇüňĹĘŔŻČÚóĹšÄçŃÇüŠÂłŠ»ĺÚÜżň║ŽŠŁąŔÇâŔÖĹ´╝îŔ┤şšŻ«ŃÇüš╗┤ń┐«ŃÇüŠÂłŠ»ĺŠłÉŠťČŔżâÚźś´╝îňŹĽŠČíńŻ┐šöĘŠŚÂÚŚ┤Ŕżâščş´╝îňĹĘŔŻČÚóĹšÄçň┐źšÜäňćůš¬ąÚĽť´╝îňŁçŠťëÔÇťŔÇŚŠŁÉňîľÔÇŁšÜ䊯ťňŐŤ´╝îŔ┐Öń║ŤÚĽťšžŹň»╣ň║öń║ćńŞşňŤŻŔ┐Ĺ7,000ńŞçńżőšÜ䊯ťňťĘŔ»ŐšľŚÚçĆ´╝îš╗ÖňŤŻń║žńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňůČňĆŞšĽÖńŞőń║ćńŞÇšëçŔôŁŠÁĚňŞéňť║ŃÇé
ňŤż´╝ÜńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞéňť║Šť║ń╝ÜŠÁőš«Ś
ńŻťńŞ║ÚźśňÇ╝ňî╗šľŚňÖĘŠó░ňĚĘňĄ┤´╝îŠ│óšžĹšÜäńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňŞâň▒Çń╗ÄńŞÄňůÂńŞÜňŐ튝ǚŤŞňů│šÜäŠ│îň░┐ňĺîŠÂłňîľňćůÚĽťň╝ÇňžőŃÇéŠ│óšžĹŠÄĘňç║ń║ćńŞľšĽîÚŽľŠČżńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íňćůÚĽťLithoVue´╝«ň돚Üäń║žňôüňŞâň▒ÇňĚ▓š╗Ćň╗Âń╝Şňł░ń║ćEXALTňŹüń║îŠîçŔéáÚĽťŃÇüŠö»Š░öš«íÚĽťŃÇüŔââÚĽť´╝îń╗ąňĆŐSpyGlassŔâćÚüôÚĽťŃÇéÚźśšź»šÜäňŞéňť║ň«ÜńŻŹ´╝îń╗ąňĆŐšżÄňŤŻň«ŻŠŁżšÜäŠö»ń╗śń╗ĚŠá╝´╝îńŻ┐ňżŚŠ│óšžĹšÜäńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťń║žňôüŠÖ«ÚüŹń╗ĚŠá╝Úźśń╝üŃÇé
AmbuŔç┤ňŐŤń║Äň╝ÇňĆĹŃÇüšöčń║žňĺîÚöÇňö«ňî╗ÚÖóňĆŐŠĽĹŠĆ┤ŠťŹňŐíÚťÇŔŽüšÜäŔ»ŐŠľşňĺîšöčňĹŻŠö»ŠîüŔ«żňĄçŃÇé2009ň╣┤´╝îAmbuŠÄĘňç║ňĆĹňŞâńŞľšĽîńŞŐšČČńŞÇńެńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŠö»Š░öš«íÚĽťaScope´╝îň╣ŠłÉńŞ║ńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŠö»Š░öš«íÚĽťÚóćňččšÜäš╗Łň»╣šÄőŔÇůŃÇéń╗ÄŠö»Š░öš«íÚĽťŔÁĚň«Â´╝îAmbuÚÇÉŠşąň«îŠłÉńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůÚĽťňůĘń║žńŞÜňŞâň▒ÇŃÇ銝ÇŔ┐ĹńŞÇńެŔ┤óň╣┤´╝îňůČňĆŞńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚöÇňö«ÚóŁňĚ▓š¬üšá┤100ńŞçŠö»ŃÇé

ňŤż´╝ÜAmbuńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňĆĹň▒ĽňĆ▓
Šł¬Ŕç│šŤ«ň돴╝îňŤŻňćůňĚ▓Šťë4ň«ÂňůČňĆŞŠÇ╗ňů▒ŔÄĚňżŚń║ć5ň╝áńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťNMPAŠ│ĘňćîŔ»ü´╝îňŁçňťĘ2020ň╣┤ŔÄĚňżŚŃÇé
ŠÖ«šöčňî╗šľŚ2014ň╣┤ŠłÉšźőń║ÄšĆáŠÁĚ´╝î2020ň╣┤6ŠťłŔÄĚňżŚńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŠ│ĘňćîŔ»ü´╝îň돊ťčňĚ▓ÚÇÜŔ┐çCEňĺîFDAŔ«ĄŔ»üň╣Âň╝ÇňÉ»ŠÁĚňĄľÚöÇňö«ŃÇéňůČňĆŞŠť¬ŠŁąń║žňôüš║┐Ŕ┐śňîůŠőČńŞÇŠČíŠÇžÚ╝╗ňĺŻňľëÚĽťŃÇüńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŠö»Š░öš«íÚĽťŃÇüńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔćÇŔâ▒ÚĽťšşëŃÇé
šĹ׊┤żňî╗šľŚ2015ň╣┤ŠłÉšźőń║Äň╣┐ňĚ×ňŤŻÚÖůšöčšëęň▓Ť´╝»ńŞÇň«ÂŠĆÉńżŤńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňż«ňłŤŠëőŠť»ŠĽ┤ńŻôŔžúňć│Šľ╣ŠíłšÜäňůĘšÉâńżŤň║öňĽć´╝îń║žňôüňĆĹň▒ĽŔžäňłĺŔŽćšŤľŠ│îň░┐ňĄľšžĹŃÇüňŽçšžĹŃÇüŔÇ│Ú╝╗ňľëšžĹŃÇüŠÂłňîľšžĹŃÇüňĹ╝ňÉŞšžĹŃÇüŠÖ«ňĄľšžĹšşëŃÇéšĹ׊┤żňî╗šľŚňťĘ2020ň╣┤ŔÄĚŠë╣ń║ćńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťňĆŐńŞÇŠČíŠÇžšöÁňşÉŔćÇŔâ▒ňćůš¬ąÚĽťŠ│ĘňćîŔ»ü´╝îňÉÂń╣芜»šŤ«ňëŹňťĘńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćňččŠîüŠťëIIIš▒╗Š│ĘňćîŔ»üŠťÇňĄÜšÜäń╝üńŞÜŃÇé
Ŕő▒Ŕ»║ń╝č2009ň╣┤ŠłÉšźőń║ÄńŞŐŠÁĚ´╝îńŞ╗ŔŽüńŞôŠ│Ęń║ÄŠÂłňîľňćůÚĽťňĺîŠ│îň░┐ňĄľšžĹšŤŞňů│ÚźśňÇ╝ŔÇŚŠŁÉšÜäšáöňĆĹňĺîÚöÇňö«´╝Ť2014ň╣┤´╝ɚźőňşÉňůČňĆŞň«ëŠŞůňî╗šľŚ´╝îŔüÜšäŽń║Äňî╗šľŚňćůš¬ąÚĽťŃÇ銝芝Ťňćůš¬ąÚĽťŔ«żňĄçŔâŻńŞÄŔÇŚŠŁÉňŻóŠłÉÚŚşšÄ»´╝îńŞ║ňż«ňłŤŠëőŠť»ŠĆÉńżŤŠĽ┤ńŻôŔžúňć│Šľ╣ŠíłŃÇé2020ň╣┤´╝îň«ëŠŞůňî╗šľŚŔÄĚŠë╣ń║ćńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽť´╝îň╣ÂňĚ▓ń║Äň돊ťčň╝Çň▒ĽŠÁĚňĄľÚöÇňö«ŃÇé
ň«ëňżŻšťüň╣ŞšŽĆňĚąňť║ňî╗šľŚŔ«żňĄçŠťëÚÖÉňůČňĆŞŠłÉšźőń║Ä2017ň╣┤´╝îń╝üńŞÜňťĘň╝ĽŔ┐ŤšżÄňŤŻšíůŔ░ĚńŞôňłęŠŐÇŠť»ňč║šíÇńŞŐ´╝îÚÇÜŔ┐çŠÂłňîľňÉŞŠöŠö╣Ŕ┐Ť´╝îšÄ░ŠőąŠťëňŤŻÚÖůÚóćňůłšÜäńŞÇŠČíŠÇžšöÁňşÉňćůš¬ąÚĽťšáöňĆĹŠŐÇŠť»ň╣│ňĆ░´╝îńŞ╗ŔŽüń╗Äń║őńŞÇŠČíŠÇžšöÁňşÉŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŃÇüŔćÇŔâ▒ŔŻ»ÚĽťšşëšÜäšáöňĆĹšöčń║ž´╝î2020ň╣┤1Šťł´╝îňůČňĆŞŔÄĚŠë╣ń║ćńŞşňŤŻÚŽľň╝áńŞÇŠČíŠÇžŔżôň░┐š«íŔŻ»ÚĽťŠ│ĘňćîŔ»üŃÇé
2020ň╣┤´╝îňćůš¬ąÚĽťňĚĘňĄ┤ňąąŠ×ŚňĚ┤Šľ»ń╗ůňçşňŹĽńŞÇń║žňôüš║┐´╝îń╗ą58.9ń║┐šżÄňůâšÜäŔÉąŠöÂŔŁëŔüöňůĘšÉâňî╗šľŚňÖĘŠó░ňůČňĆŞ100ň╝║šČČ21ňÉŹŃÇéń╗Ąń║║šżíŠůĽšÜäŔÉąŠöÂńŞÄňłęŠÂŽŔâîňÉÄ´╝»ŠŚąŠťČňĚĘňĄ┤ň»╣ń╝áš╗čňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćňččšÜäň×䊾şŃÇéńŞşňŤŻńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťňłŤńŞÜŔÇůń╗Č´╝îŔâîÚŁáńŞşňŤŻňĚĘňĄžšÜäŔôŁŠÁĚňŞéňť║´╝îŔ┐ÄŠŁąń║ćňťĘňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćňč芝ÇňąŻšÜäň╝»ÚüôŔÂůŔŻŽŠť║ń╝ÜŃÇéŔ«ęŠłĹń╗ČŠőşšŤ«ń╗ąňżů´╝îňŤŻń║žňłŤŠľ░ňůőŠťŹńŞçÚÜż´╝ÉńŞ║ńŞľšĽîńŞÇŠČíŠÇžňćůš¬ąÚĽťÚóćŔĚĹŔÇů´╝îÚÇᚎĆňůĘšÉâŠéúŔÇůŃÇé[:en]
With the development of minimally invasive surgery and early diagnosisand treatment of cancer, the application of endoscope in diagnosis andtreatment continues to increase.In 2020, thescale of domestic endoscope market has reached 25.4 billion RMB. Due to thetechnical monopoly of imported endoscope manufacturers, the market share ofdomestic players is less than 10%.Is there acounterattack opportunity similar to new-energy vehicles in the endoscopefield? What are the development trends of medical endoscope industry brought bytechnological progress?
The endoscope enters the human body through the natural orifice or thesmall incision. It is a necessary tool for examination and minimally invasivetreatment. According to the structure and shape, endoscopes can be divided intoflexible endoscopes and rigid endoscopes.
According to Frost & Sullivan data, China’s medical endoscopemarket reached 25.4 billion RMB in 2020, with a CAGR of about 14.2% from 2015to 2020. Over the same period, the global endoscope market increased from US$16.4 billion to US $21.5 billion, with a CAGR of 5.5%. The growth rate ofChina’s market is much faster than that of the world, and its share in theglobal market is increasing. The underlying reason is that the endoscope hasthe attributes of both medical equipment and consumables, the endoscope consoleis not easy to damage, and the service life of the endoscope camera ranges from6 months to 10 years. Developed countries have completed the preliminary purchaseof the endoscopes. If there is no significant innovation in technology, itisn’t easy to see substantial growth in the market.
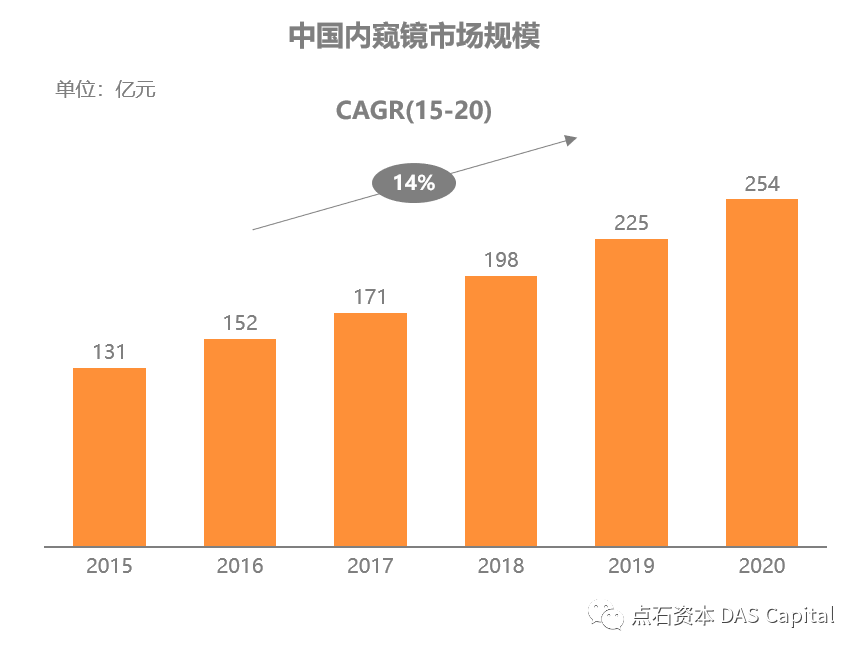
Chart: China’s MedicalEndoscope Market Size (100 Million RMB, Based on Ex-factory Price)
The domestic endoscope market in China is far from saturated. With theaccelerated penetration of early tumor screening and minimally invasivetreatment, Chinese hospitals are still increasing their purchase of endoscopesas necessary inspection and treatment tools under the promotion of foreigncompanies. At the same time, gastroscopy and colonoscopy for early cancerscreening, endoscopic surgery, and transluminal surgery, which help reducepatients’ pain and improve prognosis, have achieved rapid growth with theacceleration of China’s aging and the gradual improvement of consumption level.
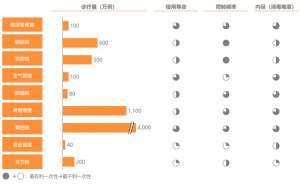
Divided by product type, in addition to rigid and flexible endoscopecameras, China’s domestic endoscope market also includes related equipment,spare parts, and therapeutic consumables for endoscopes. Excluding theinfluence of surgical consumables, subdivided by department, general surgeryaccounts for the most significant proportion of the endoscope market,corresponding to laparoscopy and choledochoscopy. The gastroenterology and urologydepartment takes the second and the third share, corresponding to gastroscopy,colonoscopy, duodenoscope and ureteroscopy, percutaneous nephroscope,cystoscopy, and other types of endoscopes, respectively.
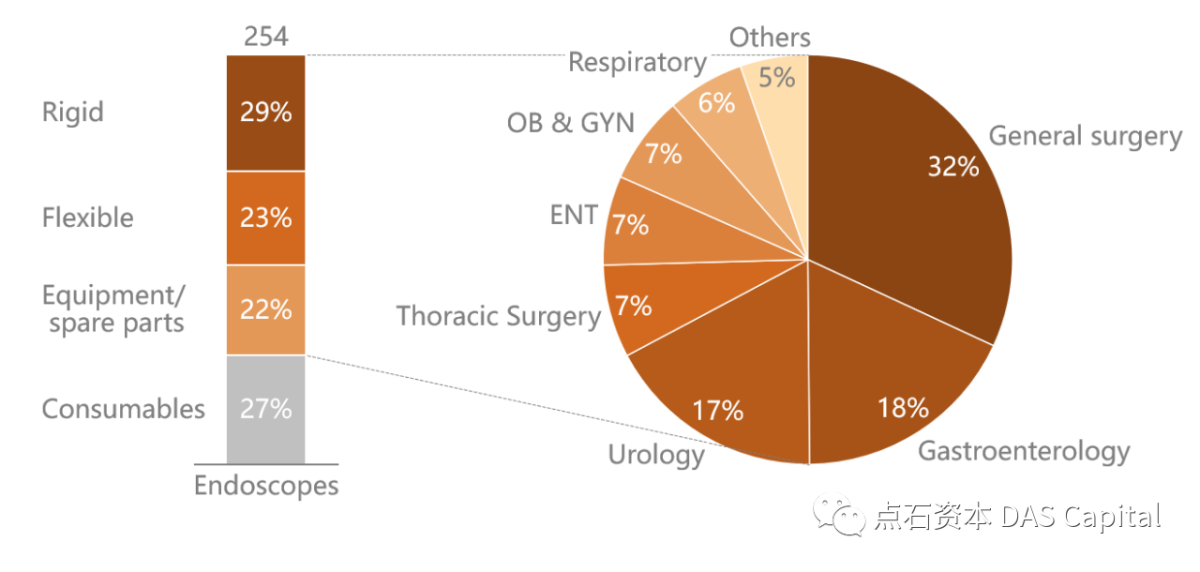
Figure: China’s Medical EndoscopeMarket Segmentation in 2020 (100 Million RMB, Based on Ex-factory Price)
Regarding competition, ChinaÔÇÖs medical endoscope market is monopolizedby Japanese and German manufacturers, and domestic manufacturers have a marketshare of ~5%. As the image sensor industry of traditional flexible endoscopesis promoted by Japanese companies, and the core technology barriers are high,Japanese companies such as Olympus, Fuji, and Pentax monopolize the flexibleendoscope market; German company Karl Storz was the first to master thecylindrical lens technology of rigid endoscopes, and German manufacturers havealways maintained a leading position in the field of rigid endoscopes. China’sdomestic rigid and flexible endoscope manufacturers, such as SonoScape Medical,Aohua Endoscopy, and Mindray Bio-Medical, cannot directly compete with importedmanufacturers in the high-end market. At present, their main target ishospitals below the second-level hospital. Among the hospitals that have beenadmitted, they are rarely used as the primary endoscope, and they are stillcatching up with their imported counterparts.
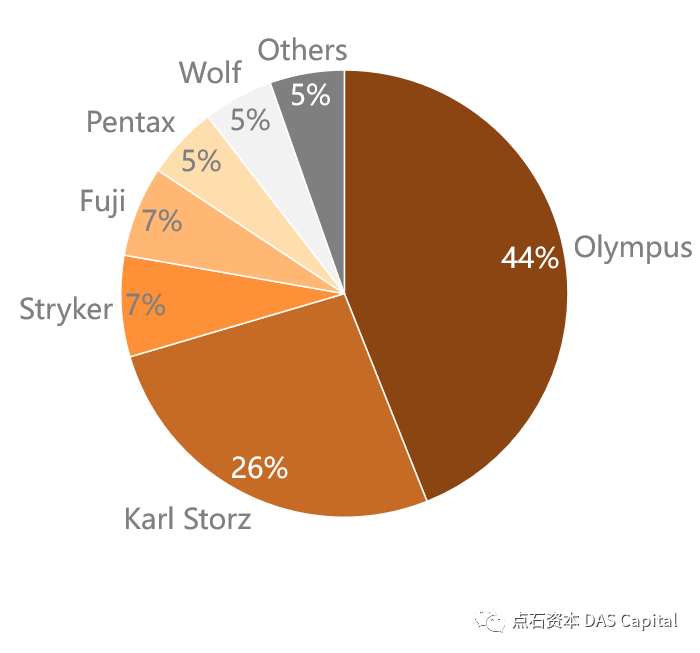
Chart: China’s Medical EndoscopeCompetitive Landscape
Domestic manufacturers have been slow to breakthrough in the field ofendoscopy, and solid technical barriers directly cause the low domesticpenetration rate. The R&D and manufacturing of endoscopes involvemulti-disciplinary and multi-field cooperation. Gastrointestinal endoscopes andureteroscopes are made of many parts, and the supply chain is highlycomplicated. The manufacturing steps are complex and cannot be fully automated.Japanese endoscope manufacturers represented by Olympus always regard the manufacturingprocess as the top secret and only produce core products in Japan.

Figure: Schematic Diagram ofthe Flexible Endoscope
The image sensors are divided into two technologies: CCD (ChargeCoupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). CCDtechnology was widely used in the early development of electronic endoscopesdue to its better image quality. However, with the improvement of CMOS in termsof color performance, the image quality and the gap with CCD are gettingsmaller and smaller, and its low energy consumption, low noise, and low-costmass production characteristics are appreciated by enterprises. Major endoscopemanufacturers gradually realize the conversion from CCD to CMOS image sensors.
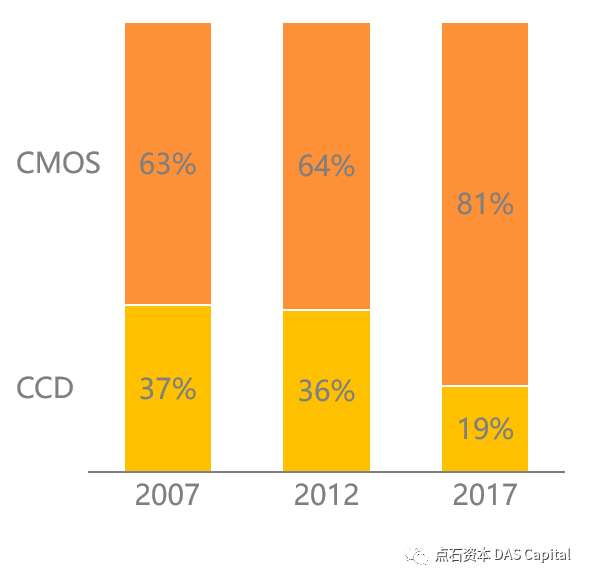
Chart: Global Image Sensor ShipmentsSegmentation
In the CCD era, CCD is an essential part of the cost of electronicendoscopes. The cost of CCD accounts for about 40% of the price of the entireendoscope. Due to the CCD design principle, the signal output is easilyaffected by a single pixel, which increases the defect rate, increases thedifficulty of manufacturing, and is costly. During the heyday of CCD, only sixcompanies could mass-produce them, namely Sony, Fuji, Kodak, Philips,Panasonic, and Sharp, four of which were Japanese companies. The leader Sonyhas a market share of over 50%, and Sony is a shareholder of Olympus, and thetwo are closely tied together. Other CCD manufacturers also impose restrictionson the export to overseas endoscope manufacturers.
Due to the high price of CCD, a long-life, sturdy and durable endoscopehas become the common choice of manufacturers and hospitals. The extremepursuit of the flexible endoscopes for maneuverability, and the contradictionbetween the performance degradation after repeated use, dramatically increasesthe manufacturing cost of the flexible endoscopes. Except for CCD, therequirements for other precision core components are also rising. These partssuppliers are concentrated in Japan and Germany. The domestic industry has notyet formed a complete industrial chain, making the competitiveness of domesticendoscope products weak.
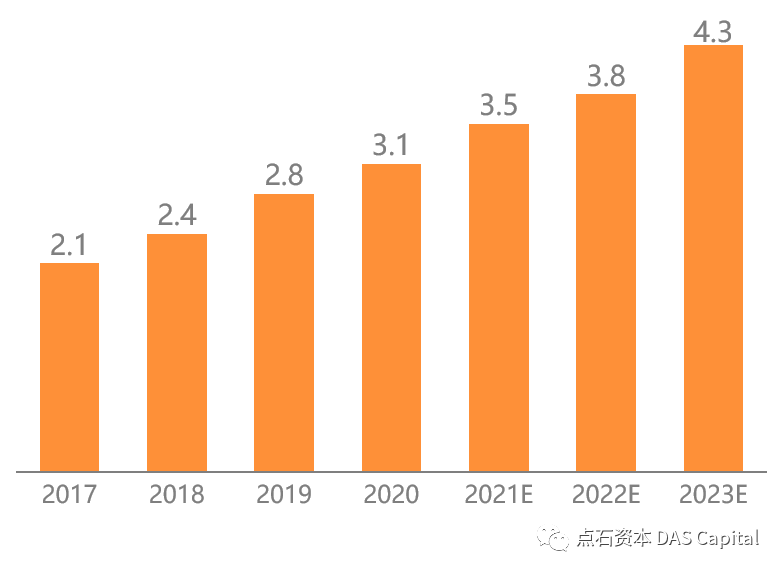
Chart: Global Shipments of MedicalCMOS
The introduction of the new technology CMOS has gotten rid ofenterprises’ dependence on CCD sensors. For example, in 2015, SonoScapedeveloped the first domestic 2-megapixel high-definition electronic endoscopesystem, HD-500, based on CMOS. What’s more gratifying is that because the CMOSmarket is more fragmented and the technical barriers are relatively low, it issuitable for large-scale mass production. The price of CMOS is showing an orderof magnitude downward trend, making the disposable endoscope possible.
When the designed service life of the endoscope is shortened fromhundreds to thousands of times to one time, and there is no need to considerthe maintainability, the cost structure of the endoscope will changedrastically. The design idea of the entire camera has changed from a precisionmechanical device to an ordinary disposable medical catheter. At the same time,the material has also changed significantly. Plastic materials replace metalmaterials, and the number of parts is reduced dramatically. Traditionalendoscope manufacturers have no time to deal with the impact of disposableendoscopes. Then Boston Scientific and Ambu, with the production experience ofmillions of annual medical consumables, have stepped on the historical stage.Domestic manufacturers have also caught up and have a role to play in theworld.
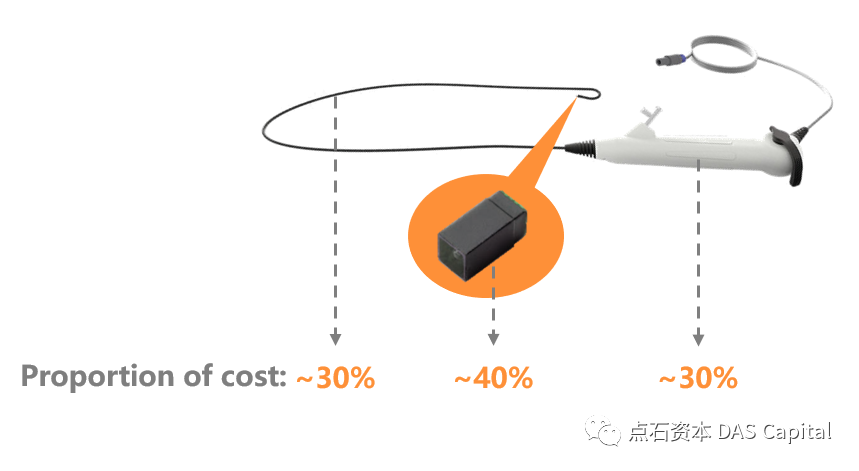
Figure: Schematic of the AverageCost of a Disposable Flexible Endoscope
An endoscope is a medical device that directly contacts the patient’sskin, mucous membrane and sterile tissues. However, because the endoscopestructure contains multiple small and long lumens, it provides an environmentfor the survival and cross-infection of microorganisms, secretions and blood. Cross-infectionbecomes an inevitable risk of medical accidents. Related academic researchshows that endoscopes rank first in the list of cross-infection risks formedical devices. More than 70% of endoscopes are not cleaned, and bacteriacontaminate nearly three-quarters of commonly used endoscopes.
In China, it is also common to report that the disinfection effect ofthe gastroscope room is not up to standard, and the biomonitoring of thegastroscope is not qualified. At the same time, more nosocomial infections arenot reported in time because they are not found. In the COVID-19 pandemic, theendoscopy rooms of many hospitals, stomatology, and ENT clinics were closedtogether, which also explained the hospital’s concern about the risk of nosocomialinfection in the endoscopy room.

Figure: 2019 Top 10 HealthTechnology Hazards by ECRI
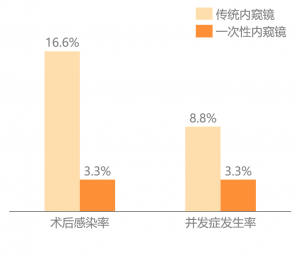
The latest study published in January 2021 showed that compared withreusable ureteroscopes, the length of hospital stay and antibiotic treatmenttime in the disposable endoscopy group were shorter, and the incidence of totalcomplications and the overall postoperative infection rate was lower. Among the90 patients under the treatment of disposable endoscopes, no uremia or bloodcultures were positive, while the control group had three positives. Itstrongly proves that disposable ureteroscope has the characteristics ofsignificantly reducing postoperative complications and infection rates.
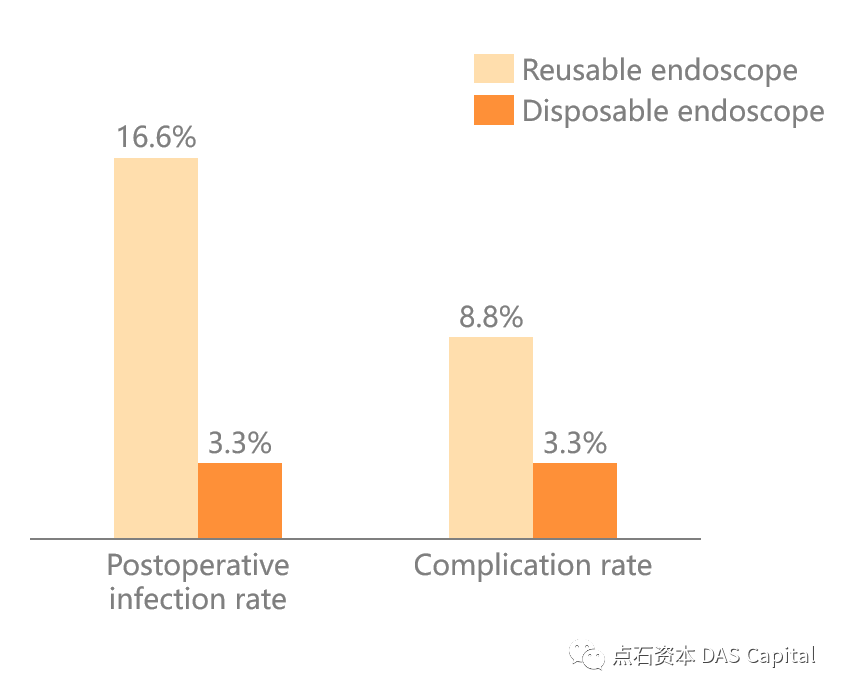
Figure: Disposable EndoscopeReduces Infection Rate After Ureteroscopy
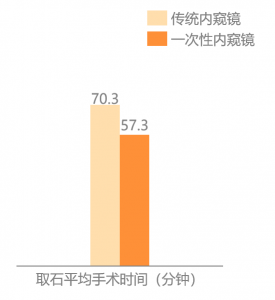
At the same time´╝îunder the workload of domestic hospitals, repeateddecontamination of endoscopes will cause the performance of reusable endoscopesto decrease or even damage. Using a disposable endoscope can ensure that theendoscope is in its best condition every time the package is unpacked, whichimproves the efficiency of the operation to a certain extent.
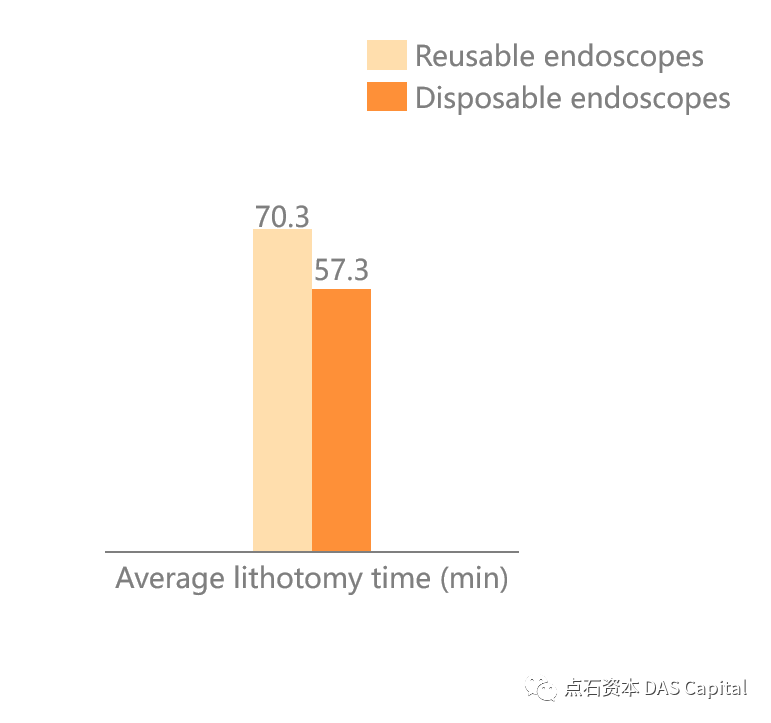
Figure: Disposable EndoscopeReduces the Operation Time of Ureteroscopy
At the same time, it is very suitable for carrying out Natural orificetransluminal endoscopic surgery for the vast county-level and lower-levelhospitals. The requirements for anesthesia and surgery are lower than that ofopen surgery. In developed countries, many endoscopies and surgeries areperformed in clinics or specialized endoscopy centers. In domestic primaryhospitals, insufficient investment in infrastructure has restricted thedevelopment of endoscopic diagnosis and treatment.
Similarly, taking ureteroscopic lithotomy as an example, if a hospitalwants to carry out this operation, it needs to purchase two imported flexibleendoscope cameras and a console, which costs about 2 million RMB. As fordisposable endoscopes, only a few domestic disposable flexible endoscope camerasand a console need to be purchased, and the price is within 100 thousand RMB. Adisposable endoscope is very conducive to the promotion of endoscopic surgeryin grass-roots hospitals.
After years of exploration by foreign and domestic companies,disposable endoscopes have become more cost-effective than durable endoscopesin many scenarios. For example, considering the life span and maintenancefrequency of the ureteroscope, a traditional reusable ureteroscopy surgerywould cost more than 12,000 RMB. The purchase price of a disposable ureteroscopefor a hospital under the same circumstance is usually less than 10,000 RMB, andthe related spending is more controllable.

Chart: Average Cost Structureof a Traditional Reusable Ureteroscopy Surgery (RMB)
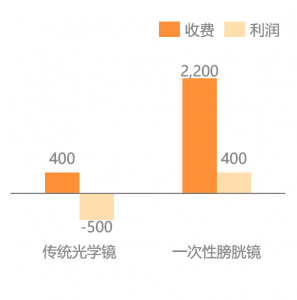
The same cost-saving benefit also applies to disposable cystoscopy. Dueto the high cost of imported electronic flexible cystoscopy, the domesticmarket is largely occupied by optical rigid cystoscopy, and hospitals usuallysuffered a 500 RMB loss per surgery on average. The disposable electronicsemi-rigid cystoscope has a smaller diameter and hydrophilic coating, offeringpatients a more expensive but comfortable surgical option, which helpscontribute to considerable net profits for hospitals.
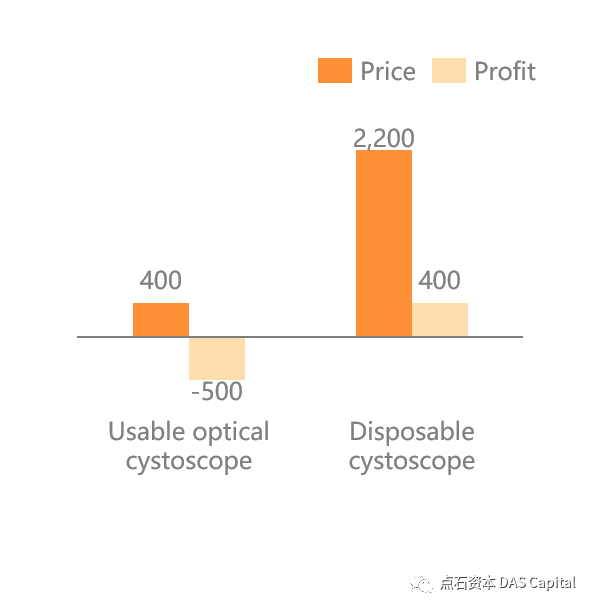
Chart: Comparison of ProfitsBetween Traditional Optical Cystoscope and Disposable Cystoscope (RMB)
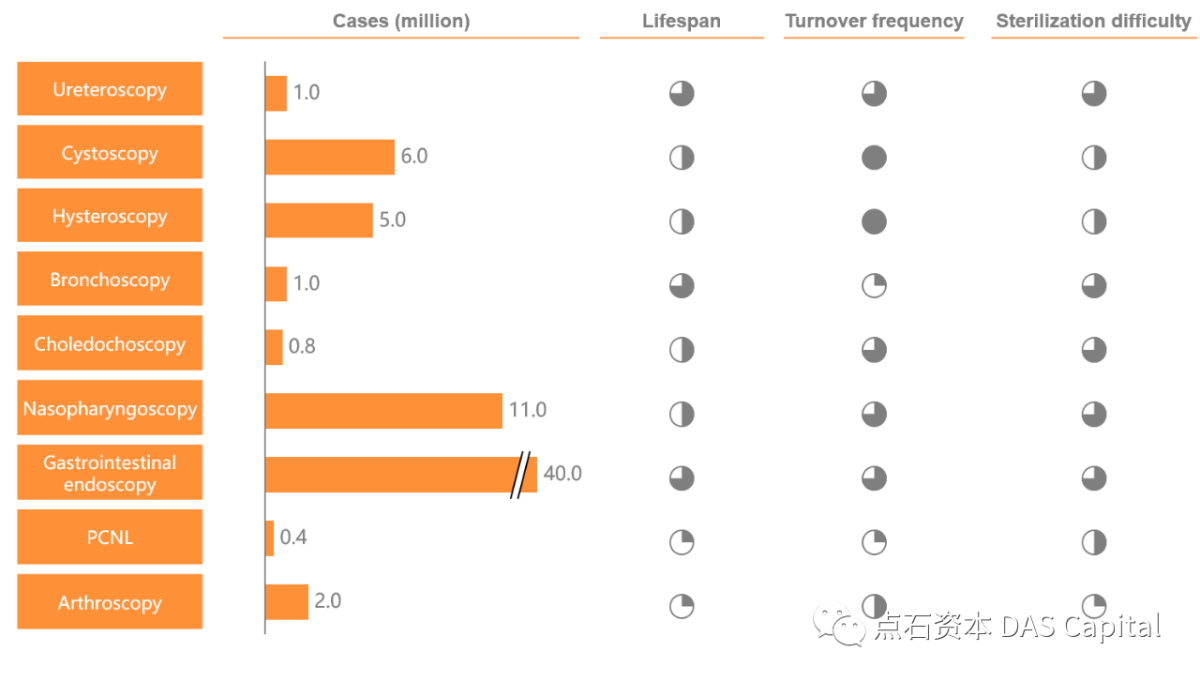
Considering the longevity, turnover, and disinfection of disposableendoscopes, endoscopes with high purchasing price, maintenance and disinfectioncosts, short usage time, and high turnover frequency are more likely to becomeÔÇťconsumablesÔÇŁ. These potential ÔÇťconsumablesÔÇŁ indicate an incredible market of70 million diagnosis and treatment cases in China, bringing blue oceans to domesticdisposable endoscope companies.
Boston Scientific
Boston Scientific, the high-value medical device giant, successfullyleveraged its experience in the urinary and digestive sectors by firstestablishing its disposable endoscope business from those two sectors. Thecompany launched┬áLithoVue, theworld’s first disposable ureteroscope on Jan 12th, 2016. The industry-leadingpipeline has later been extended to┬áEXALTD┬áduodenoscope (approved by FDA on Dec 13th,2019),┬áEXALT B┬ábronchoscope (received CE Markon May 26th, 2021), gastroscope, and┬áSpyGlass┬ácholedochoscope, etc. Boston ScientificÔÇÖs high-end marketpositioning and adequate reimbursement environment in the U.S. have jointlyresulted in those productsÔÇÖ relative-high prices.
 Ambu
Ambu A/S, founded in 1937, is a Danish company that develops, producesand markets disposable endoscopy solutions, diagnostic and life-supportingequipment to hospitals, private practices, and rescue services. In 2009, Ambulaunched aScope, the world’s first disposable bronchoscope, and later theindustry has witnessed the coronation of a long-lived king in the field ofdisposable bronchoscopy. Starting from bronchoscopy, Ambu gradually expandedits disposable endoscope kingdomÔÇÖs territory, and the sales of disposable productsexceeded 1 million in the most recent fiscal year.
Up to now, 5 domestic companies have obtained a total of 6 disposableendoscope NMPA registration certificates, most of which were obtained in 2020.
Pusen Medical
Founded in 2014, Pusen Medical is located in Zhuhai, China. The companyobtained the NMPA registration certificate of disposable ureteroscope in June2020, and had built its overseas business with CE Mark and FDA approval evenearlier. The company’s pipeline also includes disposable rhino-laryngoscopes,bronchoscopes, and cystoscopes, etc.
Redpine
Redpine was established in Guangzhou International Biological Island in2015 and aims to provide its global clients with comprehensive solutions forone-time minimally invasive surgery. Its products cover several departmentsincluding urology, gynecology, otolaryngology, gastroenterology, respiratory,and general surgery, etc. Redpine has two products currently approved, its ureteroscopeand cystoscope, both in 2020. It is also the company that holds the most ClassIII registration certificates in the field of disposable endoscopy so far.
Anqing Medical, Innovex Group
Innovex Group is composed of three independently operated enterprises,each one is active in minimal invasive consumables, disposable digitalendoscopes, and surgical energy equipment & consumables. Its disposableendoscope branch, Anqing Medical was established in 2014 and is expected tohelp form a closed-loop with both low- and high-value consumables. AnqingMedicalÔÇÖs disposable ureteroscope received NMPA approval in 2020, and same asPusen Medical, entered overseas markets prior to that.
Happiness Workshop
Anhui Happiness Workshop Medical Instruments Co., Ltd. was establishedin 2017. The company in-licensed technology from Silicon Valley and integratedthem into an international leading disposable endoscope R&D platform. Thecompany manufactures disposable ureteroscopes and cystoscopes, and obtainedNMPAÔÇÖs first approval of disposable ureteroscopy in China in Jan 2020.
North Tengda
Beijing North Tengda Technology Development Co., Ltd. was founded in2018. The company mainly engaged in domestic sales and after-sales service ofimported medical equipment, like MiroCam capsule endoscope and E.G.Scandisposable tube endoscope from South Korea. The companyÔÇÖs disposable ureteroscopyobtained NMPA approval in May 2021.
In 2020, the global endoscope leader Olympus realized $5.89 billion insales and continuously ranked 21st among the top 100 medical devicecompanies worldwide, with only endoscope products. Behind OlympusÔÇÖs enviableperformance is the strong monopoly of Japanese giants in the field of the coretechnology of traditional endoscopes. As listed above, it is the best time nowfor Chinese disposable endoscope startups to seize the opportunity and overtakeforeign conventional competitors. We are looking forward to seeing the greatvictory of domestic innovations and more and more global patients benefit from Chineseleading disposable endoscope technology.